Mar . 05, 2025 07:25 Back to list
Reno Mattress
Laying mesh for a concrete slab is an essential step in ensuring the durability, stability, and longevity of your construction project. With years of experience and in-depth expertise in the field, this guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of why mesh reinforcement is critical and how it can be effectively implemented.
Connecting the mesh sections correctly is another critical aspect of the installation process. Overlapping the sheets by at least one grid square or a minimum of 6 inches is recommended to maintain structural continuity. Secure the overlaps with tie wire to keep them from moving during the concrete pour. Meticulous attention to detail during this stage can significantly enhance the strength and durability of the finished slab. Pouring the concrete is an operation that demands precision and consistency. It's imperative to pour carefully to avoid displacing the mesh. Utilizing a pump can provide more control over the pouring process, especially for larger projects. During pouring, an even distribution of the concrete is crucial. Working it into the mesh with vibrating tools ensures that there are no air pockets and that the concrete forms a solid bond with the reinforcements. Curing is the final stage and is often underestimated. Curing involves maintaining optimal moisture, temperature, and time conditions to allow the concrete to develop strength and durability. Covering the slab with curing blankets or using curing compounds can prevent rapid moisture loss which can otherwise cause surface cracking. In conclusion, laying mesh for a concrete slab is a technical yet rewarding process that relies on proper planning, knowledgeable material selection, and meticulous installation practices. By recognizing the importance of each step—from subgrade preparation to curing—builders can create concrete slabs that are not only robust and durable but also meet the highest standards of quality and performance. The assurance of structural integrity, when backed by expertise and adherence to standards, forms the bedrock of trust in any construction endeavor.
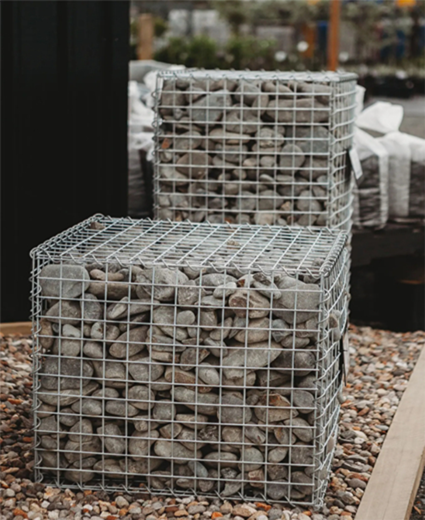


Connecting the mesh sections correctly is another critical aspect of the installation process. Overlapping the sheets by at least one grid square or a minimum of 6 inches is recommended to maintain structural continuity. Secure the overlaps with tie wire to keep them from moving during the concrete pour. Meticulous attention to detail during this stage can significantly enhance the strength and durability of the finished slab. Pouring the concrete is an operation that demands precision and consistency. It's imperative to pour carefully to avoid displacing the mesh. Utilizing a pump can provide more control over the pouring process, especially for larger projects. During pouring, an even distribution of the concrete is crucial. Working it into the mesh with vibrating tools ensures that there are no air pockets and that the concrete forms a solid bond with the reinforcements. Curing is the final stage and is often underestimated. Curing involves maintaining optimal moisture, temperature, and time conditions to allow the concrete to develop strength and durability. Covering the slab with curing blankets or using curing compounds can prevent rapid moisture loss which can otherwise cause surface cracking. In conclusion, laying mesh for a concrete slab is a technical yet rewarding process that relies on proper planning, knowledgeable material selection, and meticulous installation practices. By recognizing the importance of each step—from subgrade preparation to curing—builders can create concrete slabs that are not only robust and durable but also meet the highest standards of quality and performance. The assurance of structural integrity, when backed by expertise and adherence to standards, forms the bedrock of trust in any construction endeavor.
Next:
Latest news
-
Reinforcing Mesh: Core Material of the Construction Industry
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Welded Wire Fabric Reinvented for Modern Projects
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Superiority of Stainless Steel Woven Mesh
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Key Types of Razor Wire and Their Applications
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Durable Metal Fence Types for Security
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Best Materials for Livestock Fence
NewsJul.04,2025
STAY UPDATED
Receive special offers and first look at new
products.
products.