Oct . 19, 2024 03:22 Back to list
wire mesh gauge
Understanding Wire Mesh Gauge A Comprehensive Guide
Wire mesh is an essential material in various industries, from construction to agriculture. One of the crucial aspects of wire mesh is its gauge, which determines the thickness and strength of the wires used in the mesh. Understanding wire mesh gauge is vital for selecting the right type for your specific needs, be it for fencing, filtration, or architectural purposes.
What is Wire Mesh Gauge?
Wire mesh gauge refers to the diameter of the wire used in the mesh. It is typically measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG), where a lower number indicates a thicker wire. For instance, a 10-gauge wire is thicker than a 20-gauge wire. The gauge of the mesh directly influences its durability, weight, and overall performance in various applications.
The gauge affects not only the mesh’s structural integrity but also its flexibility and ability to withstand various environmental factors. Choosing the right gauge is essential for ensuring that the wire mesh can handle the intended load, resist corrosion, and maintain its functionality over time.
Types of Wire Mesh
Wire mesh comes in various types based on the material used, the weave, and the gauge. The most common materials include stainless steel, galvanized steel, and PVC-coated wire. For instance, stainless steel wire mesh is favored in applications where resistance to corrosion is crucial, such as in food processing or marine environments. On the other hand, galvanized wire mesh offers excellent protection against rust, making it suitable for outdoor use.
The weave pattern of the wire mesh also varies; some common types include welded wire mesh, woven wire mesh, and expanded metal mesh. Each type serves different purposes and offers distinct features. For instance, welded wire mesh is known for its high strength and rigidity, while woven wire mesh provides flexibility and is often used for airborne filtration.
wire mesh gauge
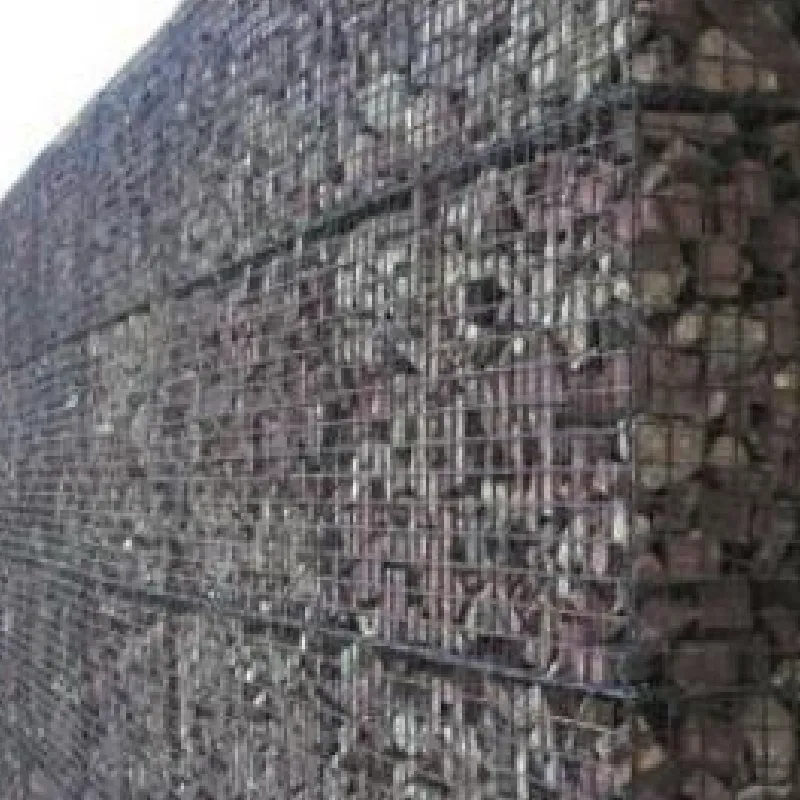

Choosing the Right Wire Mesh Gauge
When selecting wire mesh, several factors should be considered
1. Application Consider the intended use of the wire mesh. For instance, heavy-duty applications, such as construction barriers or structural supports, may require a lower gauge (thicker wire), while light-duty applications like bird fencing may suffice with a higher gauge (thinner wire).
2. Environmental Conditions If the wire mesh will be exposed to harsh weather, consider materials and gauges that offer greater resistance to corrosion and rust. Stainless steel or galvanized options might be preferable in such scenarios.
3. Load-Bearing Requirements Determine the weight and pressure the wire mesh needs to support. Thicker gauges generally provide higher strength and load-bearing capabilities, making them suitable for more demanding applications.
4. Aesthetic Considerations In architectural applications, the visual appeal of wire mesh might also play a role in the selection process. Thinner wires may create a more delicate appearance, while thicker gauges might offer a robust look.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding wire mesh gauge is crucial for selecting the appropriate mesh for your specific needs. By considering the application, environmental conditions, load-bearing requirements, and aesthetic preferences, you can make an informed choice that ensures the durability and functionality of your wire mesh. Whether you are using it for industrial applications, residential fencing, or decorative purposes, the right gauge will enhance the performance and longevity of your wire mesh. Take the time to evaluate these factors, and you’ll find that the correct gauge can provide a substantial return on investment in both safety and efficiency.
-
Reinforcing Mesh: Core Material of the Construction Industry
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Welded Wire Fabric Reinvented for Modern Projects
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Superiority of Stainless Steel Woven Mesh
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Key Types of Razor Wire and Their Applications
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Durable Metal Fence Types for Security
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Best Materials for Livestock Fence
NewsJul.04,2025
products.