Feb . 20, 2025 03:08 Back to list
road mesh for concrete
The integration of road mesh into concrete surfaces not only enhances the durability and longevity of roadways but also represents a leap in the technological evolution of civil engineering. This advancement brings forth a myriad of advantages that are redefining road construction strategies worldwide. This article delves into the experiential wisdom, professional expertise, and authoritative insights that underline why road mesh is an essential component for modern road networks.
Authoritativeness in promoting road mesh advancements comes from an array of studies and government-backed projects that validate its benefits. Research conducted by leading civil engineering institutions has consistently demonstrated that roads reinforced with mesh outperform traditional concrete pavements. Government infrastructure projects across several developed nations have mandated the use of road mesh in new roads, citing long-term benefits. This strategic move not only underscores the reliability of this innovative product but also sets a precedent for developing countries looking to enhance their road infrastructure sustainably. Trustworthiness emerges from the accountability and transparency displayed in road mesh production and implementation. Leading manufacturers of road mesh uphold stringent quality standards, ensuring that the products delivered are free of defects and tailored to withstand specific environmental and traffic conditions. This commitment to quality is bolstered by rigorous testing and compliance with international standards, thus offering stakeholders reassurance regarding the efficacy and reliability of the investment. In conclusion, the incorporation of road mesh into concrete infrastructure is not merely a trend but a substantiated leap towards constructing safer, more durable, and cost-effective roads. The collective experiences, professional insights, and authoritative endorsements strongly advocate for its broader adoption. As urban development continues to place unprecedented demands on infrastructure, technologies like road mesh offer a tangible solution to ensuring the longevity and functionality of our road networks. For civil engineers and policymakers alike, road mesh represents not just an option, but a vital component in the sustainable evolution of transportation infrastructure.
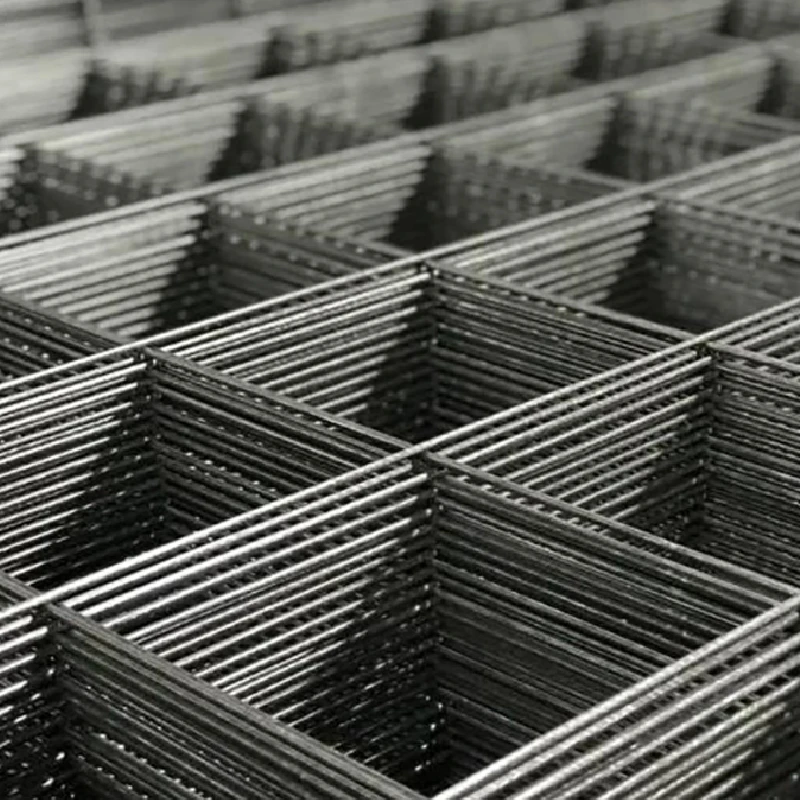
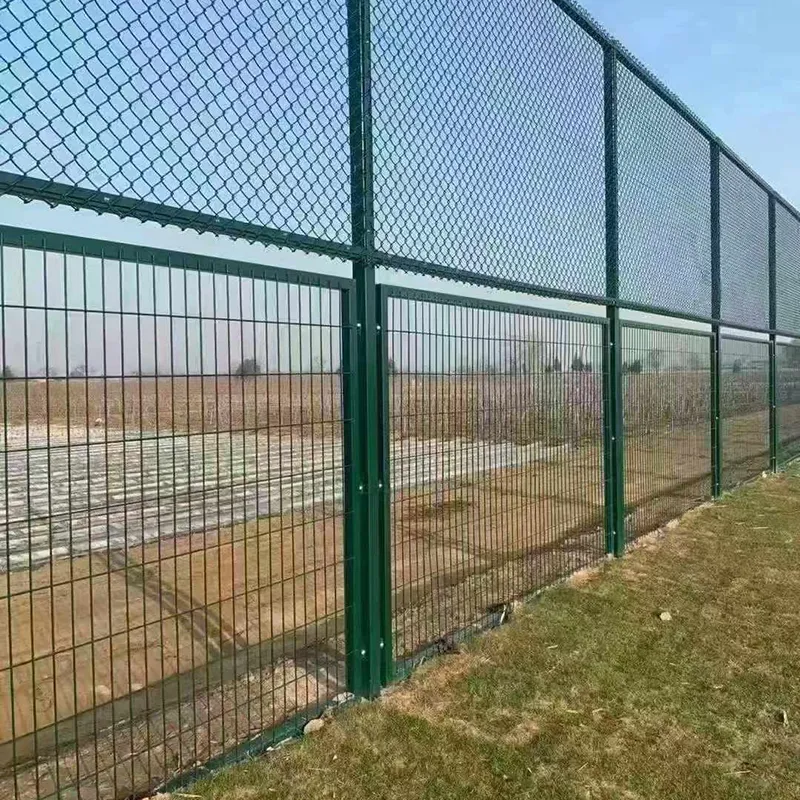


Authoritativeness in promoting road mesh advancements comes from an array of studies and government-backed projects that validate its benefits. Research conducted by leading civil engineering institutions has consistently demonstrated that roads reinforced with mesh outperform traditional concrete pavements. Government infrastructure projects across several developed nations have mandated the use of road mesh in new roads, citing long-term benefits. This strategic move not only underscores the reliability of this innovative product but also sets a precedent for developing countries looking to enhance their road infrastructure sustainably. Trustworthiness emerges from the accountability and transparency displayed in road mesh production and implementation. Leading manufacturers of road mesh uphold stringent quality standards, ensuring that the products delivered are free of defects and tailored to withstand specific environmental and traffic conditions. This commitment to quality is bolstered by rigorous testing and compliance with international standards, thus offering stakeholders reassurance regarding the efficacy and reliability of the investment. In conclusion, the incorporation of road mesh into concrete infrastructure is not merely a trend but a substantiated leap towards constructing safer, more durable, and cost-effective roads. The collective experiences, professional insights, and authoritative endorsements strongly advocate for its broader adoption. As urban development continues to place unprecedented demands on infrastructure, technologies like road mesh offer a tangible solution to ensuring the longevity and functionality of our road networks. For civil engineers and policymakers alike, road mesh represents not just an option, but a vital component in the sustainable evolution of transportation infrastructure.
Next:
Latest news
-
Reinforcing Mesh: Core Material of the Construction Industry
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Welded Wire Fabric Reinvented for Modern Projects
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Superiority of Stainless Steel Woven Mesh
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Key Types of Razor Wire and Their Applications
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Durable Metal Fence Types for Security
NewsJul.04,2025
-
Best Materials for Livestock Fence
NewsJul.04,2025
STAY UPDATED
Receive special offers and first look at new
products.
products.